All of my opinions are italicized and sources are in blue.
California’s Right to Repair Act, Senate Bill 244, has passed the state legislature. The bill passed with overwhelming approval, with a 65–0 vote in the Assembly, following a 38–0 vote in the Senate. The bill has to go back to the Senate for a minor procedural vote, and then it will await the governor’s signature.
California stands tall as the third state, after Minnesota and New York, to pass a Right to Repair law covering electronics. All three bills will collectively roll out in 2024 (January for New York and July for Minnesota and California), ensuring consumers in these states have more autonomy over their purchased devices. Together, these three states represent about 20% of the population of the United States.
This bill stands out from the laws that passed in Minnesota and New York by ensuring that repairs stay possible for longer. Manufacturers are mandated to keep repair materials, ranging from parts and tools to software and documentation, available for extended periods post-production: 3 years for products within the $50-$99.99 price bracket, and 7 years for those priced $100 or above. The bill applies to electronic and appliance products made and sold after July 1, 2021.
Some right to repair advocates are skeptical about the bill since Apple, a company that is known to be anti-repair, is in support of it. Apple is not usually a major direct lobbying force but has reportedly used its considerable heft to curb right-to-repair legislation in other states, including New York. In the New York bill, the governor added loopholes that would allow Apple to not supply any repair parts or schematics.
The only way to truly know the outcome of this bill is in 2024, if independent repair shops can receive the parts and schematics required to do their work.
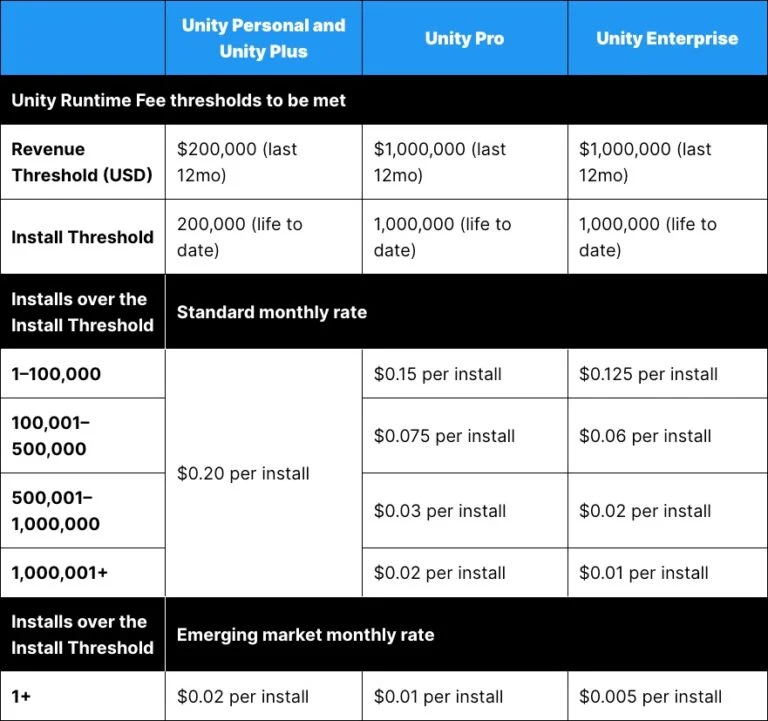
Starting on January 1, 2024, the new Unity Runtime Fee will apply to games that meet a minimum revenue threshold and have passed a minimum lifetime install count. It will also vary based on the type of Unity subscription plan the developer has.
“The Unity Runtime is code that executes on player devices and makes Made with Unity games work at scale, with billions of monthly downloads,” … “We are introducing a Unity Runtime Fee that is based upon each time a qualifying game is downloaded by an end user. We chose this because each time a game is downloaded, the Unity Runtime is also installed. … “Also we believe that an initial install-based fee allows creators to keep the ongoing financial gains from player engagement, unlike a revenue share.”
Unity in their blog-post
This caused massive backlash within the developing community. Massive Monster, devs of the roguelike game Cult of the Lamb tweeted, “Buy Cult of the Lamb now, cause we’re deleting it on January 1.” And when a commenter jokingly said it was time to pirate the game, the devs reminded that it “also counts as a Unity download.”
Other devs have voiced their concerns, with Garry Newman, the creator of Garry’s Mod, questioning the charges, “Unity can just charge us a tax per install? They can do this unilaterally? They can charge whatever they want? They can add install tracking to our game? We have to trust their tracking?”
Dani, the dev behind Muck and Crab Game pointed out that if his games were to be released with these plans, he would have owed Unity $5,600,000. Although he most likely would avoid the charge since the games were released for free.
Ireland’s Data Protection Commissioner (DPC) has fined TikTok with a 345 million euro ($368m) fine for breaching laws on the processing of children’s personal data. TikTok broke a number of EU privacy laws between July 31, 2020, and December 31, 2020 under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in relation to its processing of personal data relating to child users.
The DPC found the Family Pairing feature, which allows parents to pair their account to a child’s account and enable direct messaging, does not verify their guardian status. The DPC also found child accounts being set to public by default.

Sony launches ‘foster care’ program for aging robot dogs
LG unveils 118-inch microLED TV (For $237,000)
Intel announces Thunderbolt 5 with up to 120Gbps speeds
Qualcomm extends 5G modem deal with Apple to 2026
Google extends Chromebook support from 8 years to 10
Judge legally permabans serial Destiny 2 cheater, issues $500k judgment
Xbox Mastercard – A credit card for gamers: PlayStation launched a Visa card in 2017